Kudzu, What is it Good For?
Erosion or Invasion? Kudzu's Dilemma
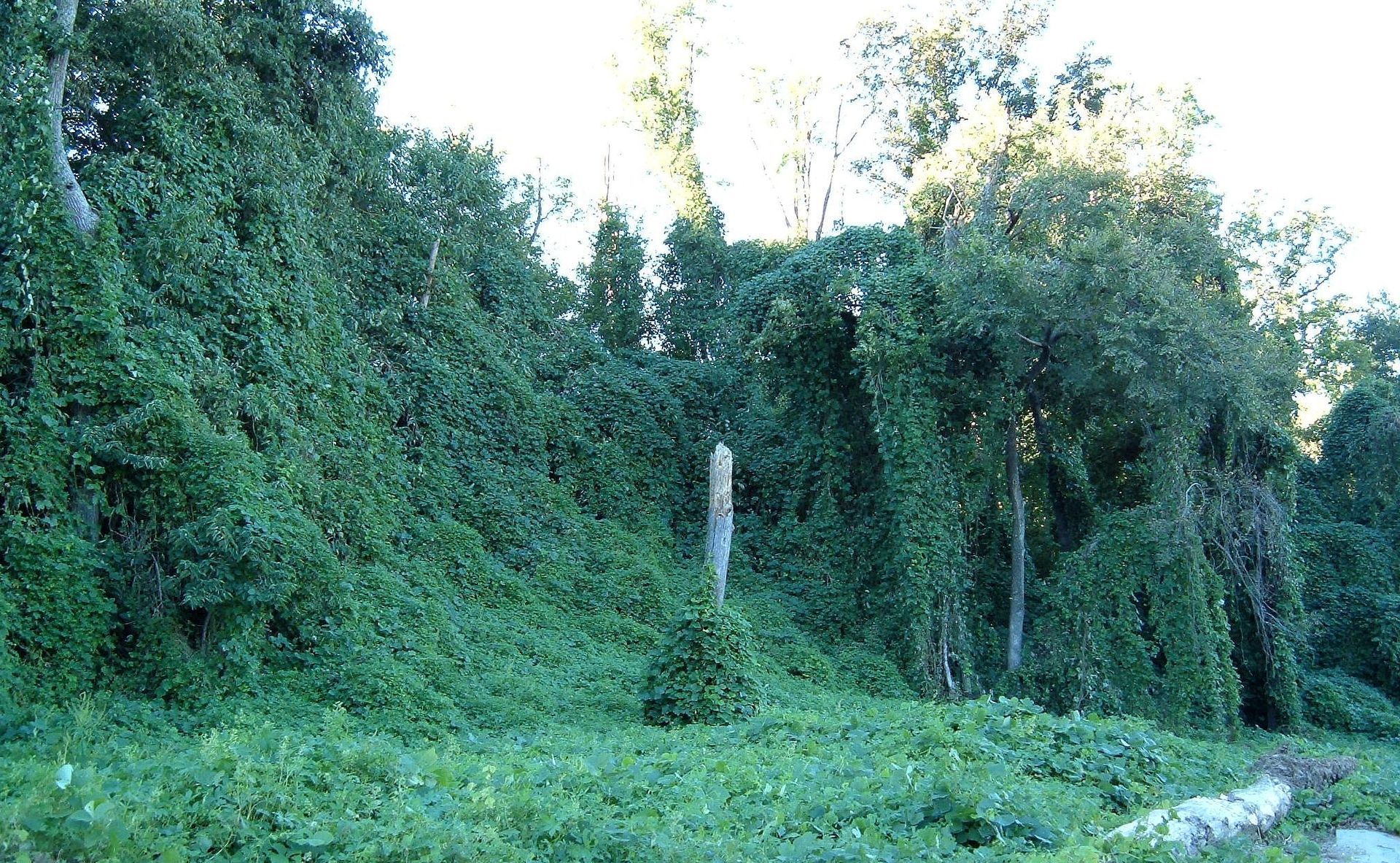

Orange Beach, Ala. – (OBA) – While most people are familiar with Kudzu if you're not, Kudzu is a climbing, coiling, and trailing vine native to East Asia, particularly Japan and China. It was introduced to the United States in the late 19th century for ornamental purposes and later promoted in the early 20th century for erosion control and to improve soil fertility. The plant's rapid growth and ability to cover almost any surface, including trees, poles, and buildings, has made it an invasive species in the southern United States. It has been said that if a cow stands in one place long enough the Kudzu will cover it up. I’ve never seen a cow covered in Kudzu but I've seen forests of trees wrapped up in it.
Kudzu grows exceptionally fast, up to a foot per day in the summer, thanks to its robust root system, which can weigh over 200 pounds and extend deep into the soil. This rapid growth allows it to outcompete native plants for sunlight, water, and nutrients, leading to significant ecological impacts. It can kill or damage other plants by smothering them under a blanket of leaves, girdling woody stems and tree trunks, and breaking branches or uprooting entire trees and shrubs through the sheer force of its weight.
The plant is hardy and thrives in a wide range of conditions but prefers sunlight, making it particularly invasive in open areas such as fields, forest edges, and roadsides. Its presence can lead to decreased biodiversity, loss of habitat for native wildlife, and difficulty in managing infested areas.
Despite its reputation as a pest, kudzu has some beneficial uses. It has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries, and its roots, leaves, and flowers are edible. The plant contains compounds with potential health benefits, including isoflavones that have been researched for their effects on menopausal symptoms, cardiovascular health, and diabetes. However, the ecological damage caused by kudzu in the United States overshadows these benefits, and efforts continue to control its spread and mitigate its impact on ecosystems.
Kudzu has been beneficial on the Eastern Shore of Mobile Bay where it has prevented erosion in gullies and cliffs along the coastline.

Share this article w/ Friends...